If you want to determine whether a furry friend is male or female, pay attention to the shape and size of specific anatomical features. Males typically have a more pronounced distance between the anus and the genital opening, while females have a shorter distance. This is often the easiest way to distinguish between them, especially in adults.
Another clear indicator is the presence of certain traits. Male felines usually exhibit larger body sizes and more robust structures. On the other hand, females tend to be smaller and more slender. If you’re observing kittens, look for tiny scrotal sacs in males; this characteristic becomes evident as they grow.
Behavior can also offer clues. Males are often more territorial and may exhibit more dominant behaviors, while females may display nurturing tendencies, especially when caring for their young. Observing these patterns over time can provide additional insights into their identities.
Identifying Feline Sex
Examine the area under the tail. Look for the distance between the opening and the anus. In males, this space is typically larger, resembling a more pronounced shape, while females have a closer proximity, appearing more like a vertical slit.
Physical Traits

Another reliable method involves observing physical characteristics. Male felines often exhibit larger body sizes and thicker necks compared to their female counterparts. Additionally, intact males may display larger, more prominent testicles, which can be seen if they are not neutered.
Behavioral Indicators
Behavior can also provide clues. Males may display more territorial behaviors, such as marking their territory with urine. In contrast, females may exhibit nurturing behaviors, especially when they are in heat or caring for kittens. Understanding these differences can assist in determining the sex of your furry friend.
For those curious about emotional connections, check out this article on how long do cats grieve. If you’re wondering about their dietary preferences, you might find it interesting to learn if they can consume spaghetti squash.
Identifying Physical Characteristics of Male and Female Felines
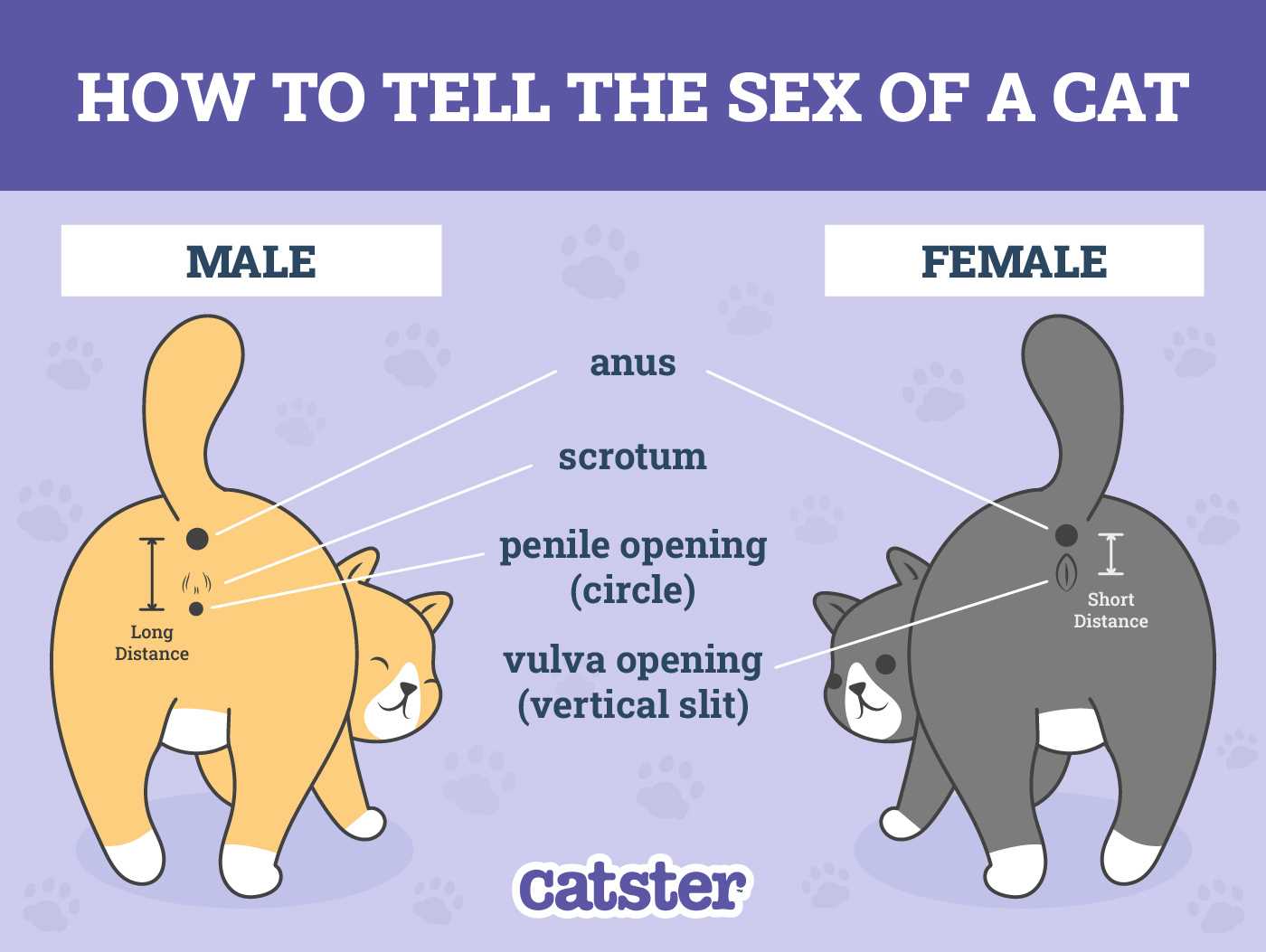
Check the space beneath the tail for specific traits. Males usually have a larger distance between the anus and the genital opening, while females have a shorter distance.
Observe the body structure. Males often possess a more robust and muscular build, while females tend to be smaller and more slender.
Examine the head shape. Males frequently display broader heads with more pronounced cheekbones, contrasting with the narrower faces of females.
Consider the size of the paws. Male felines usually have larger feet compared to females, which can be an indicator of their size difference.
Look for any distinctive markings. Some male cats, especially those with darker fur, may have more pronounced stripes or patterns than females.
Pay attention to behavioral traits. Males may exhibit more territorial behaviors, while females often show nurturing tendencies.
To summarize the physical traits:
- Distance between anus and genital area: larger in males
- Body structure: stockier in males
- Head shape: broader in males
- Paw size: larger in males
- Distinctive markings: often more pronounced in males
- Behavioral traits: territorial in males, nurturing in females
Utilizing these observations will aid in determining the sex of a feline companion accurately.
Understanding Behavioral Differences Between Male and Female Felines
Observing behavior can reveal much about whether a feline is male or female. Males typically exhibit more assertive and territorial behaviors. They often engage in marking territory through scent, which can include scratching and urine marking, especially if they are unneutered. This instinct is driven by their desire to attract mates.
On the other hand, females may display more nurturing tendencies. They often seek out cozy, safe spaces for resting, particularly if they are in heat or pregnant. Their vocalizations can also vary; females tend to be more vocal, especially when calling for mates or if they are feeling anxious or lonely.
Interactions with humans can also differ. Male felines might show more playful aggression, while females often exhibit gentler behaviors, preferring to engage in softer play. It’s common for males to initiate roughhousing, while females might choose quieter forms of interaction, such as gentle head bumps or purring for attention.
Social dynamics can also provide clues. Males might display dominance in multi-feline households, often vying for the highest perch or the most attention. Females, however, tend to form closer bonds with each other, establishing social networks that are more about cooperation than competition.
Understanding these behavioral traits can help in recognizing the differences between male and female companions. Observing their play styles, interactions, and general demeanor offers valuable insights into their unique personalities.
Utilizing Veterinary Methods for Accurate Gender Determination
For precise identification, a veterinary examination stands out as the most reliable method. A vet can perform a physical assessment and ultrasound if needed. This approach ensures clarity in distinguishing between the sexes.
Blood tests are another option. They can reveal hormonal levels specific to males or females, providing definitive answers. This method is especially useful for younger felines where physical traits may not yet be fully developed.
X-rays or advanced imaging techniques can also aid in gender identification, particularly in cases of uncertain anatomy. Vets may use these tools to visualize reproductive organs accurately.
Finally, genetic testing is available and can confirm sex through DNA analysis. This is particularly beneficial in cases where other methods might yield ambiguous results.
Recognizing Signs of Gender-Related Health Issues
Monitor urinary habits closely. Male felines are prone to urinary blockages due to their narrower urethras, while females may develop urinary tract infections more frequently. If you notice straining to urinate or blood in the urine, seek veterinary help immediately.
Watch for behavioral changes. For instance, males may exhibit more aggressive tendencies, especially if not neutered, while females might show signs of heat, such as excessive vocalization or restlessness. Any sudden shifts in behavior could indicate health problems that need addressing.
Pay attention to weight fluctuations. Obesity is a common issue among both sexes, but it can lead to different health concerns. Males may experience diabetes, while females are at risk for reproductive health issues. Regular weigh-ins can help track changes and prompt early intervention.
Inspect for skin conditions. Allergies and skin infections can affect both genders, but hormonal imbalances might lead to distinct issues. Males can develop more pronounced markings or patterns due to hormonal influences, while females might suffer from fur loss when in heat. Regular grooming helps identify these changes early.
Keep an eye on dental health. Both male and female animals can suffer from periodontal disease, but hormonal changes in females can exacerbate dental issues during heat cycles or pregnancy. Regular dental check-ups are a must for maintaining their overall well-being.
Be aware of changes in appetite. Both types can experience fluctuations, but persistent changes might signal underlying health concerns. If a male suddenly refuses food, it could be a sign of a urinary blockage, while a female’s loss of appetite might indicate an infection or other issues.
Regular veterinary visits are paramount. Annual check-ups allow for early detection of any gender-related health issues. Discuss any specific concerns with your vet regarding the unique health needs based on sex, ensuring tailored care for your furry companion.
If you want to determine whether a furry friend is male or female, pay attention to the shape and size of specific anatomical features. Males typically have a more pronounced distance between the anus and the genital opening, while females have a shorter distance. This is often the easiest way to distinguish between them, especially in adults.
Another clear indicator is the presence of certain traits. Male felines usually exhibit larger body sizes and more robust structures. On the other hand, females tend to be smaller and more slender. If you’re observing kittens, look for tiny scrotal sacs in males; this characteristic becomes evident as they grow.
Behavior can also offer clues. Males are often more territorial and may exhibit more dominant behaviors, while females may display nurturing tendencies, especially when caring for their young. Observing these patterns over time can provide additional insights into their identities.
Identifying Feline Sex
Examine the area under the tail. Look for the distance between the opening and the anus. In males, this space is typically larger, resembling a more pronounced shape, while females have a closer proximity, appearing more like a vertical slit.
Physical Traits

Another reliable method involves observing physical characteristics. Male felines often exhibit larger body sizes and thicker necks compared to their female counterparts. Additionally, intact males may display larger, more prominent testicles, which can be seen if they are not neutered.
Behavioral Indicators
Behavior can also provide clues. Males may display more territorial behaviors, such as marking their territory with urine. In contrast, females may exhibit nurturing behaviors, especially when they are in heat or caring for kittens. Understanding these differences can assist in determining the sex of your furry friend.
For those curious about emotional connections, check out this article on how long do cats grieve. If you’re wondering about their dietary preferences, you might find it interesting to learn if they can consume spaghetti squash.
Identifying Physical Characteristics of Male and Female Felines

Check the space beneath the tail for specific traits. Males usually have a larger distance between the anus and the genital opening, while females have a shorter distance.
Observe the body structure. Males often possess a more robust and muscular build, while females tend to be smaller and more slender.
Examine the head shape. Males frequently display broader heads with more pronounced cheekbones, contrasting with the narrower faces of females.
Consider the size of the paws. Male felines usually have larger feet compared to females, which can be an indicator of their size difference.
Look for any distinctive markings. Some male cats, especially those with darker fur, may have more pronounced stripes or patterns than females.
Pay attention to behavioral traits. Males may exhibit more territorial behaviors, while females often show nurturing tendencies.
To summarize the physical traits:
- Distance between anus and genital area: larger in males
- Body structure: stockier in males
- Head shape: broader in males
- Paw size: larger in males
- Distinctive markings: often more pronounced in males
- Behavioral traits: territorial in males, nurturing in females
Utilizing these observations will aid in determining the sex of a feline companion accurately.
Understanding Behavioral Differences Between Male and Female Felines
Observing behavior can reveal much about whether a feline is male or female. Males typically exhibit more assertive and territorial behaviors. They often engage in marking territory through scent, which can include scratching and urine marking, especially if they are unneutered. This instinct is driven by their desire to attract mates.
On the other hand, females may display more nurturing tendencies. They often seek out cozy, safe spaces for resting, particularly if they are in heat or pregnant. Their vocalizations can also vary; females tend to be more vocal, especially when calling for mates or if they are feeling anxious or lonely.
Interactions with humans can also differ. Male felines might show more playful aggression, while females often exhibit gentler behaviors, preferring to engage in softer play. It’s common for males to initiate roughhousing, while females might choose quieter forms of interaction, such as gentle head bumps or purring for attention.
Social dynamics can also provide clues. Males might display dominance in multi-feline households, often vying for the highest perch or the most attention. Females, however, tend to form closer bonds with each other, establishing social networks that are more about cooperation than competition.
Understanding these behavioral traits can help in recognizing the differences between male and female companions. Observing their play styles, interactions, and general demeanor offers valuable insights into their unique personalities.
Utilizing Veterinary Methods for Accurate Gender Determination
For precise identification, a veterinary examination stands out as the most reliable method. A vet can perform a physical assessment and ultrasound if needed. This approach ensures clarity in distinguishing between the sexes.
Blood tests are another option. They can reveal hormonal levels specific to males or females, providing definitive answers. This method is especially useful for younger felines where physical traits may not yet be fully developed.
X-rays or advanced imaging techniques can also aid in gender identification, particularly in cases of uncertain anatomy. Vets may use these tools to visualize reproductive organs accurately.
Finally, genetic testing is available and can confirm sex through DNA analysis. This is particularly beneficial in cases where other methods might yield ambiguous results.
Recognizing Signs of Gender-Related Health Issues
Monitor urinary habits closely. Male felines are prone to urinary blockages due to their narrower urethras, while females may develop urinary tract infections more frequently. If you notice straining to urinate or blood in the urine, seek veterinary help immediately.
Watch for behavioral changes. For instance, males may exhibit more aggressive tendencies, especially if not neutered, while females might show signs of heat, such as excessive vocalization or restlessness. Any sudden shifts in behavior could indicate health problems that need addressing.
Pay attention to weight fluctuations. Obesity is a common issue among both sexes, but it can lead to different health concerns. Males may experience diabetes, while females are at risk for reproductive health issues. Regular weigh-ins can help track changes and prompt early intervention.
Inspect for skin conditions. Allergies and skin infections can affect both genders, but hormonal imbalances might lead to distinct issues. Males can develop more pronounced markings or patterns due to hormonal influences, while females might suffer from fur loss when in heat. Regular grooming helps identify these changes early.
Keep an eye on dental health. Both male and female animals can suffer from periodontal disease, but hormonal changes in females can exacerbate dental issues during heat cycles or pregnancy. Regular dental check-ups are a must for maintaining their overall well-being.
Be aware of changes in appetite. Both types can experience fluctuations, but persistent changes might signal underlying health concerns. If a male suddenly refuses food, it could be a sign of a urinary blockage, while a female’s loss of appetite might indicate an infection or other issues.
Regular veterinary visits are paramount. Annual check-ups allow for early detection of any gender-related health issues. Discuss any specific concerns with your vet regarding the unique health needs based on sex, ensuring tailored care for your furry companion.
If you want to determine whether a furry friend is male or female, pay attention to the shape and size of specific anatomical features. Males typically have a more pronounced distance between the anus and the genital opening, while females have a shorter distance. This is often the easiest way to distinguish between them, especially in adults.
Another clear indicator is the presence of certain traits. Male felines usually exhibit larger body sizes and more robust structures. On the other hand, females tend to be smaller and more slender. If you’re observing kittens, look for tiny scrotal sacs in males; this characteristic becomes evident as they grow.
Behavior can also offer clues. Males are often more territorial and may exhibit more dominant behaviors, while females may display nurturing tendencies, especially when caring for their young. Observing these patterns over time can provide additional insights into their identities.
Identifying Feline Sex
Examine the area under the tail. Look for the distance between the opening and the anus. In males, this space is typically larger, resembling a more pronounced shape, while females have a closer proximity, appearing more like a vertical slit.
Physical Traits

Another reliable method involves observing physical characteristics. Male felines often exhibit larger body sizes and thicker necks compared to their female counterparts. Additionally, intact males may display larger, more prominent testicles, which can be seen if they are not neutered.
Behavioral Indicators
Behavior can also provide clues. Males may display more territorial behaviors, such as marking their territory with urine. In contrast, females may exhibit nurturing behaviors, especially when they are in heat or caring for kittens. Understanding these differences can assist in determining the sex of your furry friend.
For those curious about emotional connections, check out this article on how long do cats grieve. If you’re wondering about their dietary preferences, you might find it interesting to learn if they can consume spaghetti squash.
Identifying Physical Characteristics of Male and Female Felines

Check the space beneath the tail for specific traits. Males usually have a larger distance between the anus and the genital opening, while females have a shorter distance.
Observe the body structure. Males often possess a more robust and muscular build, while females tend to be smaller and more slender.
Examine the head shape. Males frequently display broader heads with more pronounced cheekbones, contrasting with the narrower faces of females.
Consider the size of the paws. Male felines usually have larger feet compared to females, which can be an indicator of their size difference.
Look for any distinctive markings. Some male cats, especially those with darker fur, may have more pronounced stripes or patterns than females.
Pay attention to behavioral traits. Males may exhibit more territorial behaviors, while females often show nurturing tendencies.
To summarize the physical traits:
- Distance between anus and genital area: larger in males
- Body structure: stockier in males
- Head shape: broader in males
- Paw size: larger in males
- Distinctive markings: often more pronounced in males
- Behavioral traits: territorial in males, nurturing in females
Utilizing these observations will aid in determining the sex of a feline companion accurately.
Understanding Behavioral Differences Between Male and Female Felines
Observing behavior can reveal much about whether a feline is male or female. Males typically exhibit more assertive and territorial behaviors. They often engage in marking territory through scent, which can include scratching and urine marking, especially if they are unneutered. This instinct is driven by their desire to attract mates.
On the other hand, females may display more nurturing tendencies. They often seek out cozy, safe spaces for resting, particularly if they are in heat or pregnant. Their vocalizations can also vary; females tend to be more vocal, especially when calling for mates or if they are feeling anxious or lonely.
Interactions with humans can also differ. Male felines might show more playful aggression, while females often exhibit gentler behaviors, preferring to engage in softer play. It’s common for males to initiate roughhousing, while females might choose quieter forms of interaction, such as gentle head bumps or purring for attention.
Social dynamics can also provide clues. Males might display dominance in multi-feline households, often vying for the highest perch or the most attention. Females, however, tend to form closer bonds with each other, establishing social networks that are more about cooperation than competition.
Understanding these behavioral traits can help in recognizing the differences between male and female companions. Observing their play styles, interactions, and general demeanor offers valuable insights into their unique personalities.
Utilizing Veterinary Methods for Accurate Gender Determination
For precise identification, a veterinary examination stands out as the most reliable method. A vet can perform a physical assessment and ultrasound if needed. This approach ensures clarity in distinguishing between the sexes.
Blood tests are another option. They can reveal hormonal levels specific to males or females, providing definitive answers. This method is especially useful for younger felines where physical traits may not yet be fully developed.
X-rays or advanced imaging techniques can also aid in gender identification, particularly in cases of uncertain anatomy. Vets may use these tools to visualize reproductive organs accurately.
Finally, genetic testing is available and can confirm sex through DNA analysis. This is particularly beneficial in cases where other methods might yield ambiguous results.
Recognizing Signs of Gender-Related Health Issues
Monitor urinary habits closely. Male felines are prone to urinary blockages due to their narrower urethras, while females may develop urinary tract infections more frequently. If you notice straining to urinate or blood in the urine, seek veterinary help immediately.
Watch for behavioral changes. For instance, males may exhibit more aggressive tendencies, especially if not neutered, while females might show signs of heat, such as excessive vocalization or restlessness. Any sudden shifts in behavior could indicate health problems that need addressing.
Pay attention to weight fluctuations. Obesity is a common issue among both sexes, but it can lead to different health concerns. Males may experience diabetes, while females are at risk for reproductive health issues. Regular weigh-ins can help track changes and prompt early intervention.
Inspect for skin conditions. Allergies and skin infections can affect both genders, but hormonal imbalances might lead to distinct issues. Males can develop more pronounced markings or patterns due to hormonal influences, while females might suffer from fur loss when in heat. Regular grooming helps identify these changes early.
Keep an eye on dental health. Both male and female animals can suffer from periodontal disease, but hormonal changes in females can exacerbate dental issues during heat cycles or pregnancy. Regular dental check-ups are a must for maintaining their overall well-being.
Be aware of changes in appetite. Both types can experience fluctuations, but persistent changes might signal underlying health concerns. If a male suddenly refuses food, it could be a sign of a urinary blockage, while a female’s loss of appetite might indicate an infection or other issues.
Regular veterinary visits are paramount. Annual check-ups allow for early detection of any gender-related health issues. Discuss any specific concerns with your vet regarding the unique health needs based on sex, ensuring tailored care for your furry companion.






