As a Scottish Fold, I know how important it is to keep an eye on my breathing patterns. Ideally, a healthy feline should have a respiratory rate between 20 to 30 breaths per minute while at rest. Monitoring this can help detect underlying health issues early on.
When I’m not playing or napping, I ensure my breathing remains steady. If I notice any changes, such as increased panting or labored breaths, it’s crucial to alert my human. They should consult a veterinarian to rule out any potential problems.
Staying calm and relaxed is key to maintaining a normal respiratory rate. Stress can lead to elevated breathing, so creating a peaceful environment is beneficial for all furry friends. Whether it’s through playtime or cozy cuddles, I always find ways to keep my spirit high and my breaths steady.
Breathing Rate for Felines
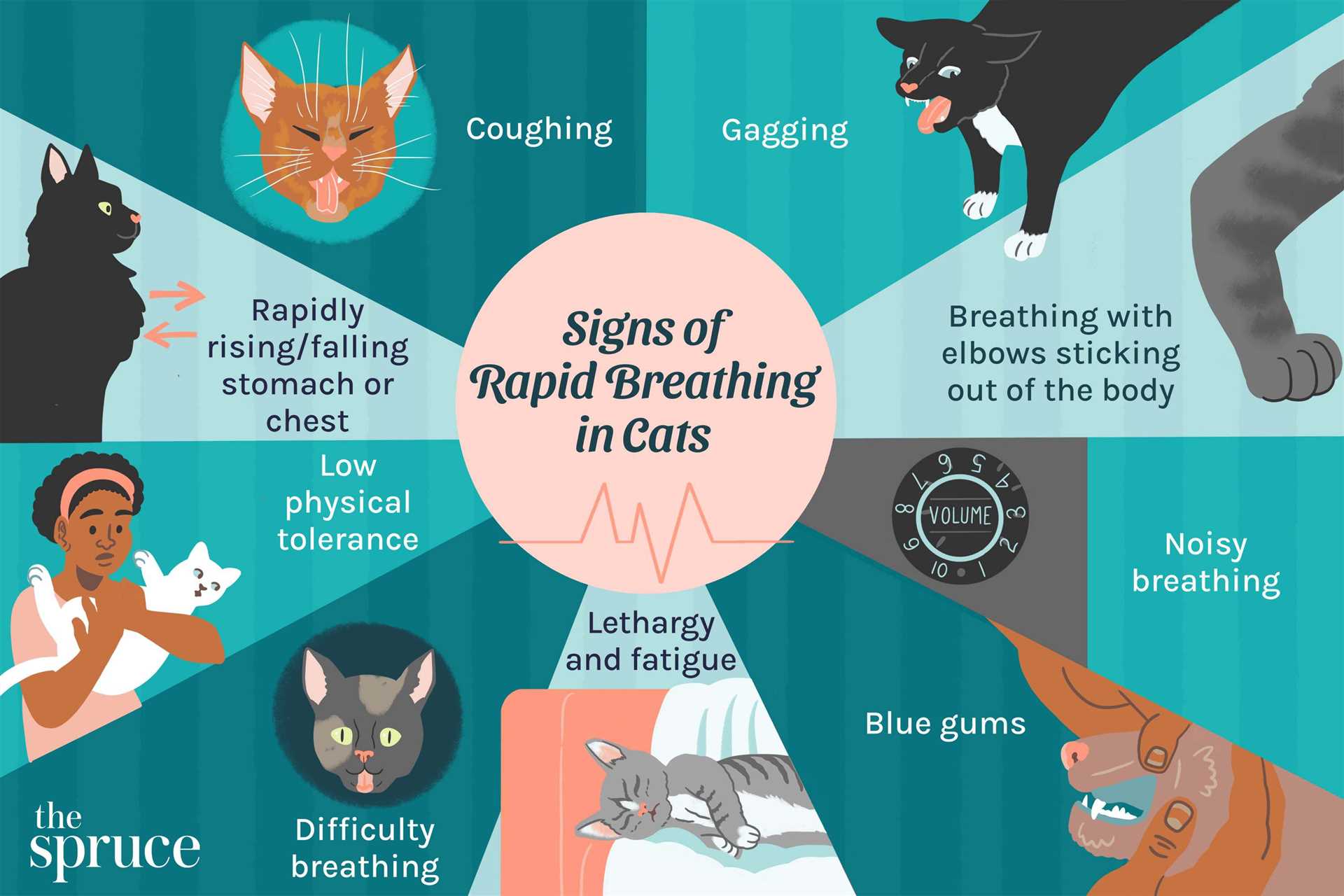
The normal respiration rate for my kind typically ranges from 20 to 30 breaths per minute while at rest. It’s crucial to monitor these numbers, as deviations can indicate health issues. If I’m panting or my breaths exceed 30 per minute, it’s time for a vet visit.
Signs of Respiratory Distress
If I show signs such as rapid inhalation and exhalation, wheezing, or open-mouth breathing, it’s a signal that something might be wrong. Observing these behaviors can help catch potential problems early.
Factors Influencing Breathing Patterns
Normal Respiratory Rates for Healthy Felines
The typical respiratory rate for a healthy feline ranges from 20 to 30 breaths per minute while at rest. This rate can vary depending on factors such as age, activity level, and overall health. It’s crucial to monitor this frequency regularly to ensure my well-being.
Factors Influencing Breathing Rates

Activities like playing or feeling anxious can temporarily elevate my breathing rate. A relaxed state, on the other hand, promotes a slower rhythm. In addition, environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity may also impact my respiratory patterns.
When to Seek Veterinary Attention
If my breathing exceeds 30 breaths per minute when resting, or if you notice any signs of distress, it’s time to consult a veterinarian. Symptoms like coughing, wheezing, or labored breathing warrant immediate attention to rule out underlying health issues.
Factors Affecting Cat Breathing Speed
Several elements influence the rate of respiration in felines, including:
- Age: Younger individuals tend to have a higher respiratory rate compared to older ones. Kittens, for instance, may breathe more rapidly.
- Activity Level: Engaging in play or physical exertion increases breathing rates. After a session of chasing toys or climbing, you might notice a quicker rhythm.
- Environment: Temperature and humidity play roles as well. Warmer, humid conditions can lead to increased ventilation needs.
- Health Status: Respiratory illnesses or infections can elevate breathing rates. Regular vet check-ups are important to monitor any changes.
- Stress Levels: Anxiety or excitement can lead to more rapid respiration. Familiarizing your feline with their surroundings can help reduce stress.
- Diet: Nutrition impacts overall health, which in turn can influence breathing patterns. Ensuring proper diet, such as knowing how much cat food a kitten should eat, is essential.
Monitoring these factors can help you understand the variations in your companion’s respiratory patterns. If you observe any significant changes, consult your veterinarian. Additionally, if your feline tends to scratch furniture, consider exploring methods on how to stop your cat from scratching your couches.
When to Seek Veterinary Help for Breathing Issues
If I notice sudden changes in my breathing patterns, such as rapid or labored inhalations, it’s time to alert my human. Any signs of distress, including wheezing, coughing, or open-mouth breathing, signal the need for immediate veterinary attention.
Persistent panting, especially when resting, suggests an underlying problem. My humans should also watch for blue-tinged gums or tongue, which indicates insufficient oxygen. If I appear lethargic or unwilling to engage in activities I typically enjoy, it’s another red flag.
In situations where I’m struggling to catch my breath, exhibiting excessive drooling, or showing signs of anxiety, my human should not hesitate to contact a veterinarian. These symptoms may point to serious conditions like pneumonia, asthma, or heart disease.
Regular monitoring of my respiratory rate during calm moments can help identify any anomalies. If my breathing exceeds the normal range for my breed or age, it warrants a trip to the vet. Early intervention can make a significant difference in recovery and overall health.
FAQ:
What is the normal breathing rate for cats?
The normal breathing rate for cats is typically between 20 to 30 breaths per minute when they are at rest. It’s important to observe your cat in a calm state, as factors like excitement, stress, or activity can temporarily increase their breathing rate. If you notice that your cat is consistently breathing faster than this rate, it may be a sign of a health issue that requires attention.
How can I measure my cat’s breathing rate accurately?
To measure your cat’s breathing rate, you can follow these steps: First, make sure your cat is relaxed and resting. You can gently place your hand on their side to feel their movements. Count the number of breaths for 15 seconds and multiply that number by four to get the breaths per minute. It’s best to do this when your cat is calm, as stress or play can skew the results. If you have concerns about the results, consult a veterinarian for further assessment.
What could cause an increase in my cat’s breathing rate?
An increase in a cat’s breathing rate, known as tachypnea, can be caused by various factors. Common reasons include physical exertion, excitement, or stress. However, it can also indicate health concerns like respiratory infections, heart disease, or pain. If you observe a persistent increase in your cat’s breathing rate, especially accompanied by other symptoms such as coughing, lethargy, or difficulty breathing, it is advisable to seek veterinary care. Early intervention can be crucial in addressing potential health issues.
As a Scottish Fold, I know how important it is to keep an eye on my breathing patterns. Ideally, a healthy feline should have a respiratory rate between 20 to 30 breaths per minute while at rest. Monitoring this can help detect underlying health issues early on.
When I’m not playing or napping, I ensure my breathing remains steady. If I notice any changes, such as increased panting or labored breaths, it’s crucial to alert my human. They should consult a veterinarian to rule out any potential problems.
Staying calm and relaxed is key to maintaining a normal respiratory rate. Stress can lead to elevated breathing, so creating a peaceful environment is beneficial for all furry friends. Whether it’s through playtime or cozy cuddles, I always find ways to keep my spirit high and my breaths steady.
Breathing Rate for Felines

The normal respiration rate for my kind typically ranges from 20 to 30 breaths per minute while at rest. It’s crucial to monitor these numbers, as deviations can indicate health issues. If I’m panting or my breaths exceed 30 per minute, it’s time for a vet visit.
Signs of Respiratory Distress
If I show signs such as rapid inhalation and exhalation, wheezing, or open-mouth breathing, it’s a signal that something might be wrong. Observing these behaviors can help catch potential problems early.
Factors Influencing Breathing Patterns
Normal Respiratory Rates for Healthy Felines
The typical respiratory rate for a healthy feline ranges from 20 to 30 breaths per minute while at rest. This rate can vary depending on factors such as age, activity level, and overall health. It’s crucial to monitor this frequency regularly to ensure my well-being.
Factors Influencing Breathing Rates

Activities like playing or feeling anxious can temporarily elevate my breathing rate. A relaxed state, on the other hand, promotes a slower rhythm. In addition, environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity may also impact my respiratory patterns.
When to Seek Veterinary Attention
If my breathing exceeds 30 breaths per minute when resting, or if you notice any signs of distress, it’s time to consult a veterinarian. Symptoms like coughing, wheezing, or labored breathing warrant immediate attention to rule out underlying health issues.
Factors Affecting Cat Breathing Speed
Several elements influence the rate of respiration in felines, including:
- Age: Younger individuals tend to have a higher respiratory rate compared to older ones. Kittens, for instance, may breathe more rapidly.
- Activity Level: Engaging in play or physical exertion increases breathing rates. After a session of chasing toys or climbing, you might notice a quicker rhythm.
- Environment: Temperature and humidity play roles as well. Warmer, humid conditions can lead to increased ventilation needs.
- Health Status: Respiratory illnesses or infections can elevate breathing rates. Regular vet check-ups are important to monitor any changes.
- Stress Levels: Anxiety or excitement can lead to more rapid respiration. Familiarizing your feline with their surroundings can help reduce stress.
- Diet: Nutrition impacts overall health, which in turn can influence breathing patterns. Ensuring proper diet, such as knowing how much cat food a kitten should eat, is essential.
Monitoring these factors can help you understand the variations in your companion’s respiratory patterns. If you observe any significant changes, consult your veterinarian. Additionally, if your feline tends to scratch furniture, consider exploring methods on how to stop your cat from scratching your couches.
When to Seek Veterinary Help for Breathing Issues
If I notice sudden changes in my breathing patterns, such as rapid or labored inhalations, it’s time to alert my human. Any signs of distress, including wheezing, coughing, or open-mouth breathing, signal the need for immediate veterinary attention.
Persistent panting, especially when resting, suggests an underlying problem. My humans should also watch for blue-tinged gums or tongue, which indicates insufficient oxygen. If I appear lethargic or unwilling to engage in activities I typically enjoy, it’s another red flag.
In situations where I’m struggling to catch my breath, exhibiting excessive drooling, or showing signs of anxiety, my human should not hesitate to contact a veterinarian. These symptoms may point to serious conditions like pneumonia, asthma, or heart disease.
Regular monitoring of my respiratory rate during calm moments can help identify any anomalies. If my breathing exceeds the normal range for my breed or age, it warrants a trip to the vet. Early intervention can make a significant difference in recovery and overall health.
FAQ:
What is the normal breathing rate for cats?
The normal breathing rate for cats is typically between 20 to 30 breaths per minute when they are at rest. It’s important to observe your cat in a calm state, as factors like excitement, stress, or activity can temporarily increase their breathing rate. If you notice that your cat is consistently breathing faster than this rate, it may be a sign of a health issue that requires attention.
How can I measure my cat’s breathing rate accurately?
To measure your cat’s breathing rate, you can follow these steps: First, make sure your cat is relaxed and resting. You can gently place your hand on their side to feel their movements. Count the number of breaths for 15 seconds and multiply that number by four to get the breaths per minute. It’s best to do this when your cat is calm, as stress or play can skew the results. If you have concerns about the results, consult a veterinarian for further assessment.
What could cause an increase in my cat’s breathing rate?
An increase in a cat’s breathing rate, known as tachypnea, can be caused by various factors. Common reasons include physical exertion, excitement, or stress. However, it can also indicate health concerns like respiratory infections, heart disease, or pain. If you observe a persistent increase in your cat’s breathing rate, especially accompanied by other symptoms such as coughing, lethargy, or difficulty breathing, it is advisable to seek veterinary care. Early intervention can be crucial in addressing potential health issues.
As a Scottish Fold, I know how important it is to keep an eye on my breathing patterns. Ideally, a healthy feline should have a respiratory rate between 20 to 30 breaths per minute while at rest. Monitoring this can help detect underlying health issues early on.
When I’m not playing or napping, I ensure my breathing remains steady. If I notice any changes, such as increased panting or labored breaths, it’s crucial to alert my human. They should consult a veterinarian to rule out any potential problems.
Staying calm and relaxed is key to maintaining a normal respiratory rate. Stress can lead to elevated breathing, so creating a peaceful environment is beneficial for all furry friends. Whether it’s through playtime or cozy cuddles, I always find ways to keep my spirit high and my breaths steady.
Breathing Rate for Felines

The normal respiration rate for my kind typically ranges from 20 to 30 breaths per minute while at rest. It’s crucial to monitor these numbers, as deviations can indicate health issues. If I’m panting or my breaths exceed 30 per minute, it’s time for a vet visit.
Signs of Respiratory Distress
If I show signs such as rapid inhalation and exhalation, wheezing, or open-mouth breathing, it’s a signal that something might be wrong. Observing these behaviors can help catch potential problems early.
Factors Influencing Breathing Patterns
Normal Respiratory Rates for Healthy Felines
The typical respiratory rate for a healthy feline ranges from 20 to 30 breaths per minute while at rest. This rate can vary depending on factors such as age, activity level, and overall health. It’s crucial to monitor this frequency regularly to ensure my well-being.
Factors Influencing Breathing Rates

Activities like playing or feeling anxious can temporarily elevate my breathing rate. A relaxed state, on the other hand, promotes a slower rhythm. In addition, environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity may also impact my respiratory patterns.
When to Seek Veterinary Attention
If my breathing exceeds 30 breaths per minute when resting, or if you notice any signs of distress, it’s time to consult a veterinarian. Symptoms like coughing, wheezing, or labored breathing warrant immediate attention to rule out underlying health issues.
Factors Affecting Cat Breathing Speed
Several elements influence the rate of respiration in felines, including:
- Age: Younger individuals tend to have a higher respiratory rate compared to older ones. Kittens, for instance, may breathe more rapidly.
- Activity Level: Engaging in play or physical exertion increases breathing rates. After a session of chasing toys or climbing, you might notice a quicker rhythm.
- Environment: Temperature and humidity play roles as well. Warmer, humid conditions can lead to increased ventilation needs.
- Health Status: Respiratory illnesses or infections can elevate breathing rates. Regular vet check-ups are important to monitor any changes.
- Stress Levels: Anxiety or excitement can lead to more rapid respiration. Familiarizing your feline with their surroundings can help reduce stress.
- Diet: Nutrition impacts overall health, which in turn can influence breathing patterns. Ensuring proper diet, such as knowing how much cat food a kitten should eat, is essential.
Monitoring these factors can help you understand the variations in your companion’s respiratory patterns. If you observe any significant changes, consult your veterinarian. Additionally, if your feline tends to scratch furniture, consider exploring methods on how to stop your cat from scratching your couches.
When to Seek Veterinary Help for Breathing Issues
If I notice sudden changes in my breathing patterns, such as rapid or labored inhalations, it’s time to alert my human. Any signs of distress, including wheezing, coughing, or open-mouth breathing, signal the need for immediate veterinary attention.
Persistent panting, especially when resting, suggests an underlying problem. My humans should also watch for blue-tinged gums or tongue, which indicates insufficient oxygen. If I appear lethargic or unwilling to engage in activities I typically enjoy, it’s another red flag.
In situations where I’m struggling to catch my breath, exhibiting excessive drooling, or showing signs of anxiety, my human should not hesitate to contact a veterinarian. These symptoms may point to serious conditions like pneumonia, asthma, or heart disease.
Regular monitoring of my respiratory rate during calm moments can help identify any anomalies. If my breathing exceeds the normal range for my breed or age, it warrants a trip to the vet. Early intervention can make a significant difference in recovery and overall health.
FAQ:
What is the normal breathing rate for cats?
The normal breathing rate for cats is typically between 20 to 30 breaths per minute when they are at rest. It’s important to observe your cat in a calm state, as factors like excitement, stress, or activity can temporarily increase their breathing rate. If you notice that your cat is consistently breathing faster than this rate, it may be a sign of a health issue that requires attention.
How can I measure my cat’s breathing rate accurately?
To measure your cat’s breathing rate, you can follow these steps: First, make sure your cat is relaxed and resting. You can gently place your hand on their side to feel their movements. Count the number of breaths for 15 seconds and multiply that number by four to get the breaths per minute. It’s best to do this when your cat is calm, as stress or play can skew the results. If you have concerns about the results, consult a veterinarian for further assessment.
What could cause an increase in my cat’s breathing rate?
An increase in a cat’s breathing rate, known as tachypnea, can be caused by various factors. Common reasons include physical exertion, excitement, or stress. However, it can also indicate health concerns like respiratory infections, heart disease, or pain. If you observe a persistent increase in your cat’s breathing rate, especially accompanied by other symptoms such as coughing, lethargy, or difficulty breathing, it is advisable to seek veterinary care. Early intervention can be crucial in addressing potential health issues.






