


It’s a common misconception that a specific hue in felines automatically determines their gender. In reality, the genetic coding behind this delightful shade is more intricate than many think. While a significant number of these charming companions are indeed boys, a notable portion can also be female.
The gene responsible for this coloration is located on the X chromosome. Males typically have one X and one Y chromosome, while females possess two X chromosomes. This genetic arrangement means that the frequency of this color can lean towards males, but it by no means excludes the possibility of females displaying this stunning coat.
So, if you encounter a delightful creature flaunting that striking orange fur, remember that gender isn’t solely defined by color. Embrace the diversity of our furry friends and appreciate the unique charm each one brings to the table.
Understanding the Genetics of Ginger Felines
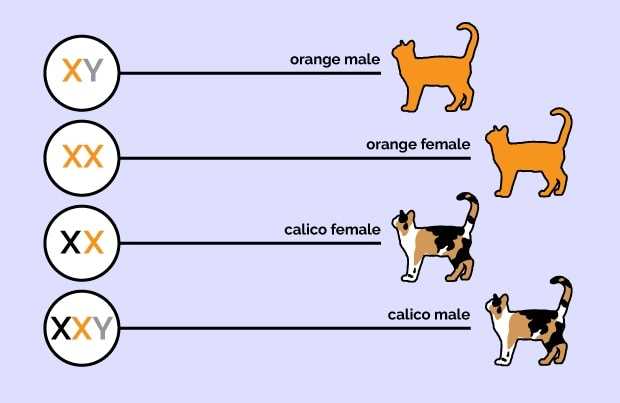
To clarify, the gene responsible for the striking ginger coat is located on the X chromosome. This means that the inheritance pattern can significantly influence the gender distribution of these furry companions.
Genetic Inheritance

When a queen carries the ginger gene, her offspring’s coat color is determined by both her genes and the male’s. Here’s how it works:
- Male offspring receive one X chromosome from their mother and a Y chromosome from their father, making them more likely to exhibit this color.
- Female kittens receive one X chromosome from each parent. If both parents have the ginger gene, then the female can express this color as well.
Factors Influencing Coloration
Several factors can affect the appearance and genetics of these felines:
- Genetic variations: Other genes can modify the base coat color, leading to different patterns.
- Environmental factors: Diet and health may play a role in the expression of coat color.
For example, a well-balanced diet influences overall coat health, and you might find it interesting to know that certain plants can be harmful to their health, affecting their appearance.
Additionally, being aware of the lifestyle preferences of these creatures can enhance their well-being. Check out what kind of music felines enjoy to create a cozy environment.
Identifying Gender Differences in Orange Tabby Cats
To determine the gender of these vibrant felines, one can look for specific physical traits. Males tend to be larger, with a more muscular build compared to their female counterparts. Additionally, males often have thicker necks and more prominent cheeks.
Behavioral Cues
Behavior also provides insight into gender. Male specimens may display more territorial behavior, marked by spraying or aggressive posturing. Females, on the other hand, often exhibit nurturing traits, showing more affection and social interaction, especially during mating seasons.
Genetic Markers

Genetic testing can clarify uncertainties. A simple DNA test can confirm the sex of any feline, revealing the chromosomal makeup. Males typically possess an XY chromosome pair, while females have XX. This method eliminates guesswork, ensuring accurate identification.
Common Myths About Ginger Felines
Many believe that a certain color of fur determines temperament. This notion suggests that those with a fiery coat are always friendly and social. In reality, personality varies widely among individuals, influenced by genetics and environment rather than mere coloration.
Myth: Only One Gender Has This Coat Color

A persistent misconception is that a specific gender exclusively sports this hue. While it’s true that a higher percentage of male representatives exhibit this coloration, females can also display it. This is tied to genetic factors, not a rule that limits this striking color to one gender.
Myth: They Are All Lazy and Laid Back
Some think that these furry companions are inherently lazy. While many enjoy lounging in sunbeams, their energy levels can vary significantly. Factors such as age, health, and individual personality play a larger role in activity levels than fur color.
Understanding these myths helps in appreciating the diversity among these charming creatures. Every individual has its unique traits, regardless of its vibrant coat. Always consider personality, behavior, and health over appearances. Each one deserves love and care tailored to their specific needs.
Factors Influencing the Population of Ginger Felines
Breeding practices significantly shape the number of these vibrant creatures. Responsible breeding ensures a balanced genetic diversity, while indiscriminate breeding can lead to health issues and a skewed gender ratio. Choosing breeders who prioritize health and temperament is crucial for maintaining a stable population.
Environmental factors also play a role. Urban areas often have higher numbers due to human interaction, whereas rural settings might see fewer due to natural predators and less human presence. Community efforts, like trap-neuter-return programs, can effectively control feral populations and improve the health of local colonies.
Genetic Considerations
Genetics directly impacts the likelihood of producing these fiery-coated companions. The gene responsible for the distinctive coat color is linked to the X chromosome. As a result, females, having two X chromosomes, have a higher chance of exhibiting this coat color compared to their male counterparts, who possess only one. This genetic trait influences population dynamics and gender distribution within the breed.
Human Preferences
People’s preferences can have a direct impact on the population. Many individuals are drawn to the striking appearance of these furry friends, leading to increased demand. Shelters and rescue organizations are vital in addressing this demand through adoption efforts. Promoting awareness about the joys of adopting rather than buying helps maintain a healthy population and gives many deserving animals a forever home.
In conclusion, a combination of breeding practices, environmental conditions, genetic traits, and human choices all contribute to the population dynamics of these unique felines. Understanding these factors aids in fostering a healthier and more balanced community of our beloved companions.
FAQ:
Are all orange tabby cats male?
No, not all orange tabby cats are male. While a majority of orange tabby cats tend to be male due to genetic factors, female orange tabbies do exist. The gene responsible for the orange color is located on the X chromosome. Since females have two X chromosomes, they can inherit the orange color from either or both parents. This means that while the ratio of male to female orange tabby cats skews towards males, females can still be orange tabbies, although they are less common.
What is the reason for the gender distribution among orange tabby cats?
The gender distribution among orange tabby cats is largely influenced by genetics. The orange coloring is linked to a specific gene on the X chromosome. Male cats have one X and one Y chromosome, so they only need one copy of the orange gene to display the orange tabby coloration. In contrast, female cats have two X chromosomes, which means they need two copies of the orange gene to be orange. As a result, more male cats are orange tabbies because they only require one copy of the gene, while females require two. This genetic mechanism results in a higher prevalence of orange tabby males compared to females.
It’s a common misconception that a specific hue in felines automatically determines their gender. In reality, the genetic coding behind this delightful shade is more intricate than many think. While a significant number of these charming companions are indeed boys, a notable portion can also be female.
The gene responsible for this coloration is located on the X chromosome. Males typically have one X and one Y chromosome, while females possess two X chromosomes. This genetic arrangement means that the frequency of this color can lean towards males, but it by no means excludes the possibility of females displaying this stunning coat.
So, if you encounter a delightful creature flaunting that striking orange fur, remember that gender isn’t solely defined by color. Embrace the diversity of our furry friends and appreciate the unique charm each one brings to the table.
Understanding the Genetics of Ginger Felines

To clarify, the gene responsible for the striking ginger coat is located on the X chromosome. This means that the inheritance pattern can significantly influence the gender distribution of these furry companions.
Genetic Inheritance

When a queen carries the ginger gene, her offspring’s coat color is determined by both her genes and the male’s. Here’s how it works:
- Male offspring receive one X chromosome from their mother and a Y chromosome from their father, making them more likely to exhibit this color.
- Female kittens receive one X chromosome from each parent. If both parents have the ginger gene, then the female can express this color as well.
Factors Influencing Coloration
Several factors can affect the appearance and genetics of these felines:
- Genetic variations: Other genes can modify the base coat color, leading to different patterns.
- Environmental factors: Diet and health may play a role in the expression of coat color.
For example, a well-balanced diet influences overall coat health, and you might find it interesting to know that certain plants can be harmful to their health, affecting their appearance.
Additionally, being aware of the lifestyle preferences of these creatures can enhance their well-being. Check out what kind of music felines enjoy to create a cozy environment.
Identifying Gender Differences in Orange Tabby Cats
To determine the gender of these vibrant felines, one can look for specific physical traits. Males tend to be larger, with a more muscular build compared to their female counterparts. Additionally, males often have thicker necks and more prominent cheeks.
Behavioral Cues
Behavior also provides insight into gender. Male specimens may display more territorial behavior, marked by spraying or aggressive posturing. Females, on the other hand, often exhibit nurturing traits, showing more affection and social interaction, especially during mating seasons.
Genetic Markers

Genetic testing can clarify uncertainties. A simple DNA test can confirm the sex of any feline, revealing the chromosomal makeup. Males typically possess an XY chromosome pair, while females have XX. This method eliminates guesswork, ensuring accurate identification.
Common Myths About Ginger Felines
Many believe that a certain color of fur determines temperament. This notion suggests that those with a fiery coat are always friendly and social. In reality, personality varies widely among individuals, influenced by genetics and environment rather than mere coloration.
Myth: Only One Gender Has This Coat Color

A persistent misconception is that a specific gender exclusively sports this hue. While it’s true that a higher percentage of male representatives exhibit this coloration, females can also display it. This is tied to genetic factors, not a rule that limits this striking color to one gender.
Myth: They Are All Lazy and Laid Back
Some think that these furry companions are inherently lazy. While many enjoy lounging in sunbeams, their energy levels can vary significantly. Factors such as age, health, and individual personality play a larger role in activity levels than fur color.
Understanding these myths helps in appreciating the diversity among these charming creatures. Every individual has its unique traits, regardless of its vibrant coat. Always consider personality, behavior, and health over appearances. Each one deserves love and care tailored to their specific needs.
Factors Influencing the Population of Ginger Felines
Breeding practices significantly shape the number of these vibrant creatures. Responsible breeding ensures a balanced genetic diversity, while indiscriminate breeding can lead to health issues and a skewed gender ratio. Choosing breeders who prioritize health and temperament is crucial for maintaining a stable population.
Environmental factors also play a role. Urban areas often have higher numbers due to human interaction, whereas rural settings might see fewer due to natural predators and less human presence. Community efforts, like trap-neuter-return programs, can effectively control feral populations and improve the health of local colonies.
Genetic Considerations
Genetics directly impacts the likelihood of producing these fiery-coated companions. The gene responsible for the distinctive coat color is linked to the X chromosome. As a result, females, having two X chromosomes, have a higher chance of exhibiting this coat color compared to their male counterparts, who possess only one. This genetic trait influences population dynamics and gender distribution within the breed.
Human Preferences
People’s preferences can have a direct impact on the population. Many individuals are drawn to the striking appearance of these furry friends, leading to increased demand. Shelters and rescue organizations are vital in addressing this demand through adoption efforts. Promoting awareness about the joys of adopting rather than buying helps maintain a healthy population and gives many deserving animals a forever home.
In conclusion, a combination of breeding practices, environmental conditions, genetic traits, and human choices all contribute to the population dynamics of these unique felines. Understanding these factors aids in fostering a healthier and more balanced community of our beloved companions.
FAQ:
Are all orange tabby cats male?
No, not all orange tabby cats are male. While a majority of orange tabby cats tend to be male due to genetic factors, female orange tabbies do exist. The gene responsible for the orange color is located on the X chromosome. Since females have two X chromosomes, they can inherit the orange color from either or both parents. This means that while the ratio of male to female orange tabby cats skews towards males, females can still be orange tabbies, although they are less common.
What is the reason for the gender distribution among orange tabby cats?
The gender distribution among orange tabby cats is largely influenced by genetics. The orange coloring is linked to a specific gene on the X chromosome. Male cats have one X and one Y chromosome, so they only need one copy of the orange gene to display the orange tabby coloration. In contrast, female cats have two X chromosomes, which means they need two copies of the orange gene to be orange. As a result, more male cats are orange tabbies because they only require one copy of the gene, while females require two. This genetic mechanism results in a higher prevalence of orange tabby males compared to females.
It’s a common misconception that a specific hue in felines automatically determines their gender. In reality, the genetic coding behind this delightful shade is more intricate than many think. While a significant number of these charming companions are indeed boys, a notable portion can also be female.
The gene responsible for this coloration is located on the X chromosome. Males typically have one X and one Y chromosome, while females possess two X chromosomes. This genetic arrangement means that the frequency of this color can lean towards males, but it by no means excludes the possibility of females displaying this stunning coat.
So, if you encounter a delightful creature flaunting that striking orange fur, remember that gender isn’t solely defined by color. Embrace the diversity of our furry friends and appreciate the unique charm each one brings to the table.
Understanding the Genetics of Ginger Felines

To clarify, the gene responsible for the striking ginger coat is located on the X chromosome. This means that the inheritance pattern can significantly influence the gender distribution of these furry companions.
Genetic Inheritance

When a queen carries the ginger gene, her offspring’s coat color is determined by both her genes and the male’s. Here’s how it works:
- Male offspring receive one X chromosome from their mother and a Y chromosome from their father, making them more likely to exhibit this color.
- Female kittens receive one X chromosome from each parent. If both parents have the ginger gene, then the female can express this color as well.
Factors Influencing Coloration
Several factors can affect the appearance and genetics of these felines:
- Genetic variations: Other genes can modify the base coat color, leading to different patterns.
- Environmental factors: Diet and health may play a role in the expression of coat color.
For example, a well-balanced diet influences overall coat health, and you might find it interesting to know that certain plants can be harmful to their health, affecting their appearance.
Additionally, being aware of the lifestyle preferences of these creatures can enhance their well-being. Check out what kind of music felines enjoy to create a cozy environment.
Identifying Gender Differences in Orange Tabby Cats
To determine the gender of these vibrant felines, one can look for specific physical traits. Males tend to be larger, with a more muscular build compared to their female counterparts. Additionally, males often have thicker necks and more prominent cheeks.
Behavioral Cues
Behavior also provides insight into gender. Male specimens may display more territorial behavior, marked by spraying or aggressive posturing. Females, on the other hand, often exhibit nurturing traits, showing more affection and social interaction, especially during mating seasons.
Genetic Markers

Genetic testing can clarify uncertainties. A simple DNA test can confirm the sex of any feline, revealing the chromosomal makeup. Males typically possess an XY chromosome pair, while females have XX. This method eliminates guesswork, ensuring accurate identification.
Common Myths About Ginger Felines
Many believe that a certain color of fur determines temperament. This notion suggests that those with a fiery coat are always friendly and social. In reality, personality varies widely among individuals, influenced by genetics and environment rather than mere coloration.
Myth: Only One Gender Has This Coat Color

A persistent misconception is that a specific gender exclusively sports this hue. While it’s true that a higher percentage of male representatives exhibit this coloration, females can also display it. This is tied to genetic factors, not a rule that limits this striking color to one gender.
Myth: They Are All Lazy and Laid Back
Some think that these furry companions are inherently lazy. While many enjoy lounging in sunbeams, their energy levels can vary significantly. Factors such as age, health, and individual personality play a larger role in activity levels than fur color.
Understanding these myths helps in appreciating the diversity among these charming creatures. Every individual has its unique traits, regardless of its vibrant coat. Always consider personality, behavior, and health over appearances. Each one deserves love and care tailored to their specific needs.
Factors Influencing the Population of Ginger Felines
Breeding practices significantly shape the number of these vibrant creatures. Responsible breeding ensures a balanced genetic diversity, while indiscriminate breeding can lead to health issues and a skewed gender ratio. Choosing breeders who prioritize health and temperament is crucial for maintaining a stable population.
Environmental factors also play a role. Urban areas often have higher numbers due to human interaction, whereas rural settings might see fewer due to natural predators and less human presence. Community efforts, like trap-neuter-return programs, can effectively control feral populations and improve the health of local colonies.
Genetic Considerations
Genetics directly impacts the likelihood of producing these fiery-coated companions. The gene responsible for the distinctive coat color is linked to the X chromosome. As a result, females, having two X chromosomes, have a higher chance of exhibiting this coat color compared to their male counterparts, who possess only one. This genetic trait influences population dynamics and gender distribution within the breed.
Human Preferences
People’s preferences can have a direct impact on the population. Many individuals are drawn to the striking appearance of these furry friends, leading to increased demand. Shelters and rescue organizations are vital in addressing this demand through adoption efforts. Promoting awareness about the joys of adopting rather than buying helps maintain a healthy population and gives many deserving animals a forever home.
In conclusion, a combination of breeding practices, environmental conditions, genetic traits, and human choices all contribute to the population dynamics of these unique felines. Understanding these factors aids in fostering a healthier and more balanced community of our beloved companions.
FAQ:
Are all orange tabby cats male?
No, not all orange tabby cats are male. While a majority of orange tabby cats tend to be male due to genetic factors, female orange tabbies do exist. The gene responsible for the orange color is located on the X chromosome. Since females have two X chromosomes, they can inherit the orange color from either or both parents. This means that while the ratio of male to female orange tabby cats skews towards males, females can still be orange tabbies, although they are less common.
What is the reason for the gender distribution among orange tabby cats?
The gender distribution among orange tabby cats is largely influenced by genetics. The orange coloring is linked to a specific gene on the X chromosome. Male cats have one X and one Y chromosome, so they only need one copy of the orange gene to display the orange tabby coloration. In contrast, female cats have two X chromosomes, which means they need two copies of the orange gene to be orange. As a result, more male cats are orange tabbies because they only require one copy of the gene, while females require two. This genetic mechanism results in a higher prevalence of orange tabby males compared to females.








