


It’s a surprising fact that some felines may consume their young ones. This behavior can arise from various reasons, often linked to instinctual responses and environmental factors. For instance, a mother may sense that her offspring are unhealthy or not viable, prompting her to cull them for the sake of the rest of her litter.
Stressful conditions can also trigger such actions. If a feline feels threatened or perceives danger, she might resort to drastic measures to protect herself and her surviving offspring. Inadequate resources, such as food or shelter, can further exacerbate this instinct, leading to an unfortunate decision to sacrifice some of her young.
Understanding these behaviors is crucial for those caring for felines. Providing a safe, secure environment is vital, as is ensuring that the mother has access to sufficient nutrition. This can significantly reduce the likelihood of such distressing behaviors occurring.
Understanding Maternal Behavior in Felines
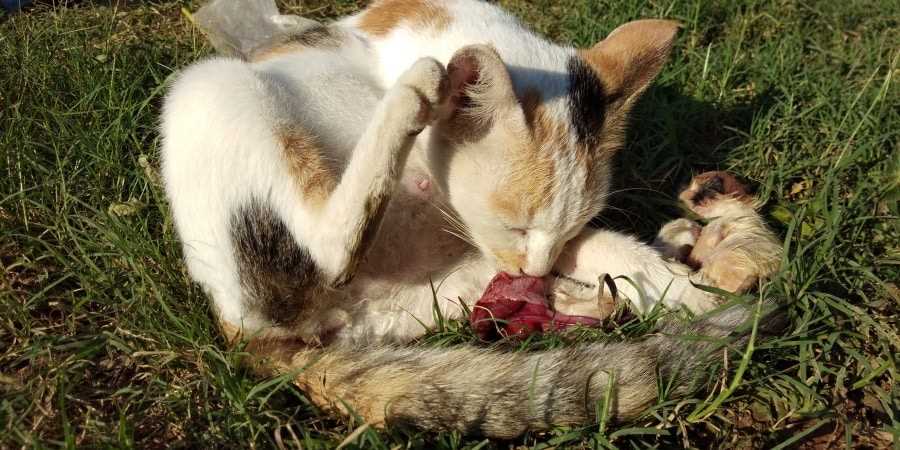

In certain circumstances, a female feline may show unusual behavior towards her offspring. If a mother perceives any health issues or abnormalities in her young, she might instinctively eliminate them. This is a natural response aimed at preserving the vitality of the rest of her litter.
Common Reasons for Such Actions
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| Health Complications | Offspring with visible defects or illnesses may be seen as liabilities. |
| Stress Factors | A stressful environment can trigger protective instincts leading to drastic decisions. |
| Lack of Resources | Insufficient food or shelter may prompt a mother to prioritize stronger young. |
Behavioral Insights
It’s crucial to observe the surroundings of a new family. If conditions are not optimal, intervention may be necessary. Providing a safe space with adequate nutrition can mitigate some of these risks. Familiarizing oneself with signs of distress in a mother can lead to timely assistance, ensuring her mental well-being and that of her young.
Understanding Maternal Instincts in Cats
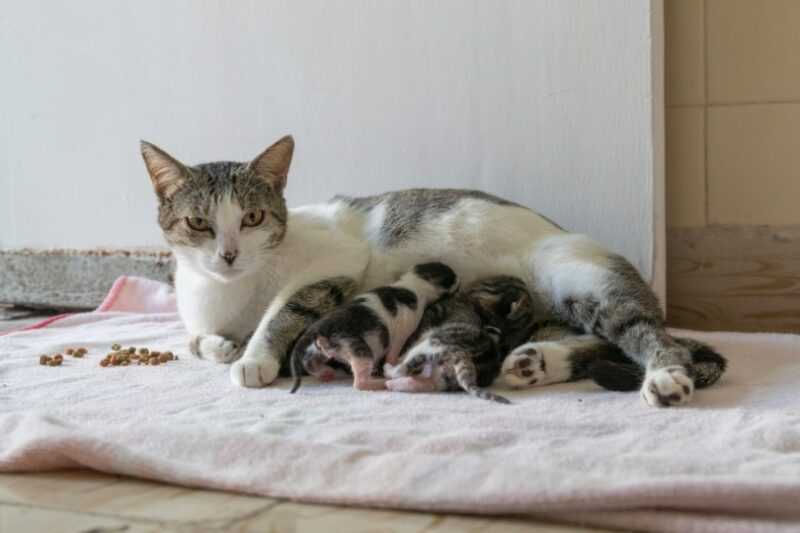

It’s crucial to recognize that nurturing behaviors arise from instinctual drives. Felines possess a strong urge to protect and care for their offspring. This bond can sometimes lead to unexpected behaviors, particularly when stress levels are high or if health issues arise within the litter.
For pregnant or nursing females, environmental factors play a significant role. A quiet, safe space is essential for them to feel secure. If they sense danger or instability, their instinct may lead them to remove perceived threats, which could include weaker or sickly young.
Nutrition is another key component. A balanced diet during gestation and lactation influences the overall well-being of both the mother and her young. Insufficient nourishment can lead to behavioral changes, as the mother may instinctively prioritize her survival over the survival of her young.
It’s also important to monitor the health of the kittens. If any are not thriving, the mother might instinctively act to eliminate them from the environment. This is a harsh reality of nature, driven by the survival of the fittest concept.
For those interested in maintaining a healthy environment for all creatures, understanding how to lower alkalinity in a reef tank can be beneficial. You can find more about it here.
Identifying Signs of Stress in Mother Cats
Watch for excessive grooming. If a feline starts to groom more than usual, it might indicate anxiety. This behavior often leads to bald patches or skin irritations.
Observe eating habits closely. A decrease in appetite or sudden food hoarding can signal distress. Conversely, overeating may also occur as a coping mechanism.
Changes in vocalization are significant. Increased yowling or growling may suggest discomfort or fear, while an unusual silence could indicate withdrawal from interaction.
Body Language Indicators
Pay attention to tail position. A low or puffed-up tail often reflects insecurity, while an arched back can signify aggression or fright. These signals require careful observation.
Ears that flick or flatten against the head indicate unease. If the feline regularly turns away or hides, it may be overwhelmed by its surroundings.
Social Interactions
Monitor how she interacts with her young. If she appears overly aggressive or neglectful, it could be a sign of stress. A lack of nurturing behaviors might suggest emotional strain.
Consider any recent changes in the environment. New pets, loud noises, or unfamiliar visitors can create tension, so assess the surroundings to identify potential stressors.
Exploring Nutritional Deficiencies and Impacts
Imbalanced nutrition can lead to severe consequences in felines, particularly during the delicate stages of motherhood. A lack of essential nutrients may trigger behaviors that seem perplexing, including the abandonment or harm of offspring. It’s crucial to ensure a balanced diet to support both the parent and her young.
Key Nutrients to Monitor
- Protein: High-quality protein is vital for energy and growth. Insufficient protein intake can lead to lethargy and reduced maternal care.
- Vitamins: Vitamins A, D, E, and B-complex play significant roles in metabolism and overall health. A deficiency might manifest in poor coat condition and weakened immune responses.
- Minerals: Calcium and phosphorus are critical for skeletal development in kittens. Low levels can result in complications for both mother and her litter.
Supplementing Diets
Consider integrating supplements to address any potential deficiencies. Always consult a veterinarian before making changes to dietary regimens. This ensures that any added nutrients align with specific needs, especially during nursing periods.
Keep in mind the importance of a holistic approach to care. Regular veterinary check-ups can help detect underlying health issues early. For instance, addressing ear conditions with appropriate ear mite meds for cats can contribute to overall well-being.
Focusing on nutrition and health not only supports a nurturing environment but also enhances the likelihood of thriving offspring. This proactive stance can mitigate stress and anxiety, promoting a healthier dynamic in the household.
Assessing the Role of Illness in Feline Behavior
Understanding how sickness influences actions can be alarming. Affected felines may exhibit unusual tendencies, including neglecting offspring. Regular check-ups with a veterinarian are paramount to detect any underlying health issues.
Symptoms such as lethargy, lack of appetite, or changes in grooming habits might indicate illness. If a feline shows signs of distress or abnormal behavior, monitoring closely and consulting a vet is advisable. Early detection of conditions like infections or metabolic disorders can prevent further complications.
Consider maintaining a stress-free environment. High levels of anxiety can exacerbate health problems, leading to detrimental behaviors. Implementing calming techniques, such as providing safe spaces and minimizing noise, can foster well-being.
Nutrition plays a significant role; deficiencies can impact physical and mental health. Ensure a balanced diet tailored to specific needs, particularly during pregnancy or nursing. Supplementing with high-quality nutrients may mitigate risks associated with health issues.
In summary, staying vigilant about health and environmental factors is crucial for the well-being of both mothers and their young. Prioritize veterinary care and maintain a nurturing atmosphere to support positive behavior. This proactive approach can make a significant difference in overall health and behavior.
Analyzing Environmental Factors and Their Influence
Ensure a calm setting for the young ones. Noise, overcrowding, or sudden changes can trigger anxiety in a nurturing feline. Open spaces should be avoided; a cozy, secluded area promotes safety and comfort.
Monitor the temperature. Extreme heat or cold can affect maternal behavior. A warm, draft-free location is optimal for both the caretaker and her offspring.
Limit human interaction during the initial days. Frequent handling can stress a nurturing feline, making her more prone to isolating or rejecting her young. Allow her to bond naturally in a private environment.
Evaluate the presence of other animals. Aggressive or overly curious pets can increase stress levels, resulting in negative outcomes. Create a barrier if necessary to keep the environment tranquil.
Observe daily routines. Disruptions, such as changes in feeding times or litter box access, can lead to confusion and unease. Consistency helps maintain a stable atmosphere.
Consider the role of previous experiences. A nurturing feline with a traumatic past may exhibit unpredictable behavior. Patience and understanding are key in these situations.
Steps to Support a New Mother Cat and Her Kittens

Provide a quiet, safe space for the new family. Choose a secluded area away from heavy foot traffic and noise. This helps reduce stress for the feline and her offspring.
Ensure Proper Nutrition
Offer high-quality, nutrient-rich food specifically designed for nursing felines. This supports her energy needs and ensures sufficient milk production for her young.
Always have fresh water available. Hydration is crucial during this period.
Monitor Health and Behavior
Regularly check for any signs of illness or distress. Look for changes in appetite, behavior, or any unusual sounds from the young ones. Promptly consult a veterinarian if any concerns arise.
Keep the environment clean and free from hazards. Remove any potential threats that could harm the little ones or the mother.
Provide gentle social interaction. Spend time close by but allow her to approach when she feels comfortable. This helps build trust and offers emotional support.
Be attentive to her needs. Adjust her environment if she shows signs of discomfort or anxiety. Simple changes can make a significant difference in her well-being.







